Myopia or short-sightedness is a type of refractive error in which parallel rays of light coming from infinity are focused in front of the retina when accommodation is at rest.

Varieties of Myopia
- Axial myopia results from increase in anteroposterior length of the eyeball. It is the commonest form.
- Curvatural myopia occurs due to increased curvature of the cornea, lens or both.
- Positional myopia is produced by anterior placement of crystalline lens in the eye.
- Index myopia results from increase in the refractive index of crystalline lens associated with nuclear sclerosis.
- Myopia due to excessive accommodation occurs in patients with spasm of accommodation
- Congenital myopia present since birth, however,is usually diagnosed by the age of 2-3 years.
- Simple or developmental myopia considered as a physiological error not associated with any disease of the eye. Its prevalence increases from 2% at 5 years to 14% at 15 years of age. Since the sharpest rise occurs at school going age i.e., between 8 year to 12 years so, it is also called school myopia.
- Pathological or degenerative myopia is a rapidly progressive error which starts in childhood at 5-10 years of age and results in high myopia during early adult life which is usually associated with degenerative changes in the eye.
- Acquired myopia which may be: (i) post-traumatic; (ii) post-keratitic; (iii) drug-induced, (iv) pseudomyopia; (v )space myopia; (vii) night myopia; and (viii) consecutive myopia.
Symptoms of myopia
- Asthenopic symptoms (ocular fatigue, discomfort, lacrimation, and headaches) may occur in patients with small degree of myopia.
- Poor vision for distance (short-sightedness) is the main symptom of myopia. There is considerable failure in visual function as the error is usually high. Further, due to progressive degenerative changes, an uncorrectable loss of vision may occur.
- Half shutting of the eyes may be complained by parents of the child. The child does so to achieve the greater clarity of vision.
- Muscae volitantes i.e., floating black opacities in front of the eyes are also complained of by many patients. These occur due to degenerated liquefied vitreous.
- Night blindness may be complained by very high myopes having marked degenerative changes.
Treatment of myopia
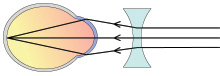
- Optical treatment of myopia constitutes prescription of appropriate concave (minus power lense) lenses, so that clear image is formed on the retina.
- The basic rule of correcting myopia is converse of that in hypermetropia, i.e., the minimum acceptance providing maximum vision should be prescribed. In very high myopia undercorrection is always better to avoid the problem of near vision and that of minification of images.
2.Surgical treatment of myopia is becoming very popular now-a-days.
3.General measures empirically believed to effect the progress of myopia (unproven usefulness) include balanced diet rich in vitamins and proteins and early management of associated debilitating disease.
4.Low vision aids (LVA) are indicated in patients of progressive myopia with advanced degenerative changes, where useful vision cannot be obtained with spectacles and contact lenses.


